1# plain.admin
2
3**Manage your app with a backend interface.**
4
5The Plain Admin provides a combination of built-in views and the flexibility to create your own. You can use it to quickly get visibility into your app's data and to manage it.
6
7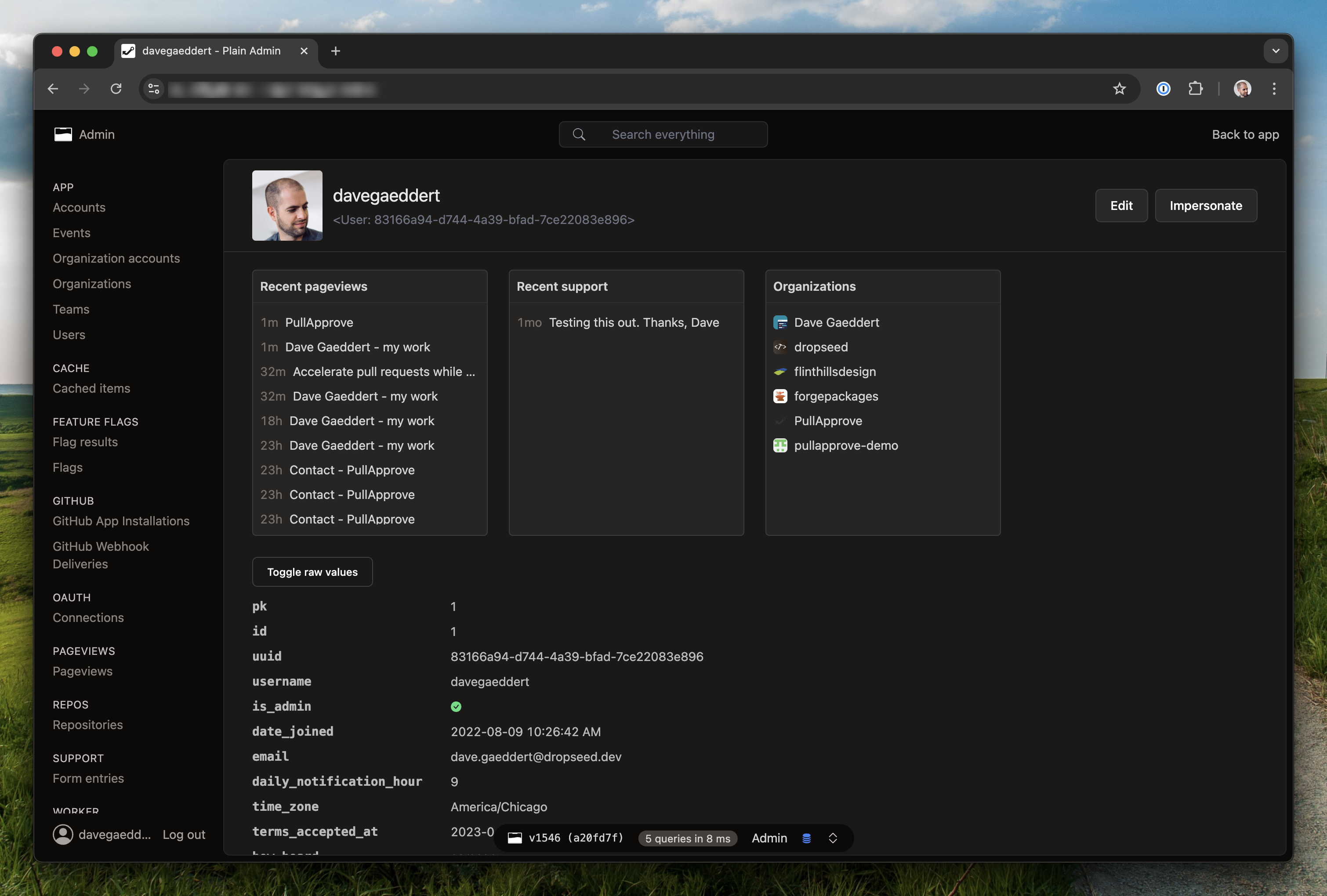
8
9## Installation
10
11Install the `plain.admin` package and its dependencies.
12
13```console
14uv add plain.admin
15```
16
17The admin uses a combination of other Plain packages, most of which you will already have installed. Ultimately, your settings will look something like this:
18
19```python
20# app/settings.py
21INSTALLED_PACKAGES = [
22 "plain.models",
23 "plain.tailwind",
24 "plain.auth",
25 "plain.sessions",
26 "plain.htmx",
27 "plain.admin",
28 "plain.elements",
29 # other packages...
30]
31
32AUTH_USER_MODEL = "users.User"
33AUTH_LOGIN_URL = "login"
34
35MIDDLEWARE = [
36 "plain.sessions.middleware.SessionMiddleware",
37 "plain.auth.middleware.AuthenticationMiddleware",
38 "plain.admin.AdminMiddleware",
39]
40```
41
42Your User model is expected to have an `is_admin` field (or attribute) for checking who has permission to access the admin.
43
44```python
45# app/users/models.py
46from plain import models
47
48
49@models.register_model
50class User(models.Model):
51 is_admin = models.BooleanField(default=False)
52 # other fields...
53```
54
55To make the admin accessible, add the `AdminRouter` to your root URLs.
56
57```python
58# app/urls.py
59from plain.admin.urls import AdminRouter
60from plain.urls import Router, include, path
61
62from . import views
63
64
65class AppRouter(Router):
66 namespace = ""
67 urls = [
68 include("admin/", AdminRouter),
69 path("login/", views.LoginView, name="login"),
70 path("logout/", LogoutView, name="logout"),
71 # other urls...
72 ]
73
74```
75
76Optionally, you can add the admin toolbar to your base template. The toolbar will appear when `settings.DEBUG` or when `request.user.is_admin` (including in production!).
77
78```html
79<!-- app/templates/base.html -->
80<!DOCTYPE html>
81<html lang="en">
82<head>
83 <meta charset="UTF-8">
84 <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
85 <title>{{ html_title|default("My App") }}</title>
86 {% tailwind_css %}
87</head>
88<body>
89 {% block content required %}{% endblock %}
90
91 {% toolbar %}
92</body>
93</html>
94```
95
96## Admin viewsets
97
98The most common use of the admin is to display and manage your `plain.models`. To do this, create a viewset with a set of inner views.
99
100```python
101# app/users/admin.py
102from plain.admin.views import (
103 AdminModelDetailView,
104 AdminModelListView,
105 AdminModelUpdateView,
106 AdminViewset,
107 register_viewset,
108)
109from plain.models.forms import ModelForm
110
111from .models import User
112
113
114class UserForm(ModelForm):
115 class Meta:
116 model = User
117 fields = ["email"]
118
119
120@register_viewset
121class UserAdmin(AdminViewset):
122 class ListView(AdminModelListView):
123 model = User
124 fields = [
125 "id",
126 "email",
127 "created_at__date",
128 ]
129 queryset_order = ["-created_at"]
130 search_fields = [
131 "email",
132 ]
133
134 class DetailView(AdminModelDetailView):
135 model = User
136
137 class UpdateView(AdminModelUpdateView):
138 template_name = "admin/users/user_form.html"
139 model = User
140 form_class = UserForm
141```
142
143The [`AdminViewset`](./views/viewsets.py) will automatically recognize inner views named `ListView`, `CreateView`, `DetailView`, `UpdateView`, and `DeleteView`. It will interlink these views automatically in the UI and form success URLs. You can define additional views too, but you will need to implement a couple methods to hook them up.
144
145## Admin cards
146
147TODO
148
149## Admin forms
150
151TODO
152
153## List `displays`
154
155On admin list views, you can define different `displays` to build predefined views of your data. The display choices will be shown in the UI, and you can use the current `self.display` in your view.
156
157```python
158# app/users/admin.py
159from plain.admin.views import AdminModelListView, register_viewset
160
161from .models import User
162
163
164@register_viewset
165class UserAdmin(AdminViewset):
166 class ListView(AdminModelListView):
167 model = User
168 fields = [
169 "id",
170 "email",
171 "created_at__date",
172 ]
173 displays = ["Users without email"]
174
175 def get_objects(self):
176 objects = super().get_objects()
177
178 if self.display == "Users without email":
179 objects = objects.filter(email="")
180
181 return objects
182```
183
184## Toolbar
185
186TODO
187
188## Impersonate
189
190TODO