# plain.admin
**Manage your app with a backend interface.**
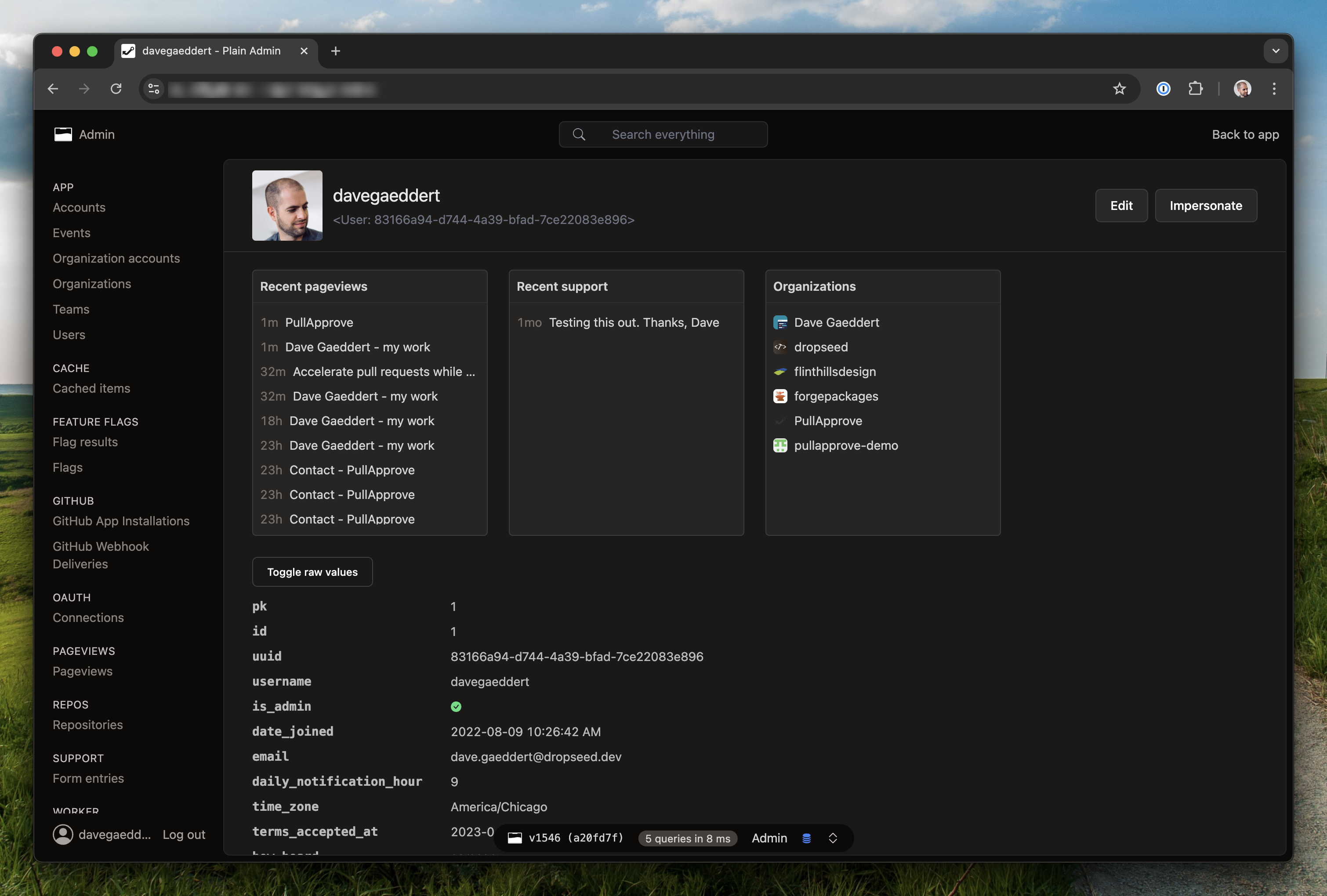
The Plain Admin provides a combination of built-in views and the flexibility to create your own. You can use it to quickly get visibility into your app's data and to manage it.
## Installation
Install the `plain.admin` package and its dependencies.
```console
uv add plain.admin
```
The admin uses a combination of other Plain packages, most of which you will already have installed. Ultimately, your settings will look something like this:
```python
# app/settings.py
INSTALLED_PACKAGES = [
"plain.models",
"plain.tailwind",
"plain.auth",
"plain.sessions",
"plain.htmx",
"plain.admin",
"plain.elements",
# other packages...
]
AUTH_USER_MODEL = "users.User"
AUTH_LOGIN_URL = "login"
MIDDLEWARE = [
"plain.sessions.middleware.SessionMiddleware",
"plain.auth.middleware.AuthenticationMiddleware",
"plain.admin.AdminMiddleware",
]
```
Your User model is expected to have an `is_admin` field (or attribute) for checking who has permission to access the admin.
```python
# app/users/models.py
from plain import models
@models.register_model
class User(models.Model):
is_admin = models.BooleanField(default=False)
# other fields...
```
To make the admin accessible, add the `AdminRouter` to your root URLs.
```python
# app/urls.py
from plain.admin.urls import AdminRouter
from plain.urls import Router, include, path
from . import views
class AppRouter(Router):
namespace = ""
urls = [
include("admin/", AdminRouter),
path("login/", views.LoginView, name="login"),
path("logout/", LogoutView, name="logout"),
# other urls...
]
```
Optionally, you can add the admin toolbar to your base template. The toolbar will appear when `settings.DEBUG` or when `request.user.is_admin` (including in production!).
```html
{{ html_title|default("My App") }}
{% tailwind_css %}
{% block content required %}{% endblock %}
{% toolbar %}
```
## Admin viewsets
The most common use of the admin is to display and manage your `plain.models`. To do this, create a viewset with a set of inner views.
```python
# app/users/admin.py
from plain.admin.views import (
AdminModelDetailView,
AdminModelListView,
AdminModelUpdateView,
AdminViewset,
register_viewset,
)
from plain.models.forms import ModelForm
from .models import User
class UserForm(ModelForm):
class Meta:
model = User
fields = ["email"]
@register_viewset
class UserAdmin(AdminViewset):
class ListView(AdminModelListView):
model = User
fields = [
"id",
"email",
"created_at__date",
]
queryset_order = ["-created_at"]
search_fields = [
"email",
]
class DetailView(AdminModelDetailView):
model = User
class UpdateView(AdminModelUpdateView):
template_name = "admin/users/user_form.html"
model = User
form_class = UserForm
```
The [`AdminViewset`](https://plainframework.com/docs/plain-admin/plain/admin/views/viewsets.py?llm) will automatically recognize inner views named `ListView`, `CreateView`, `DetailView`, `UpdateView`, and `DeleteView`. It will interlink these views automatically in the UI and form success URLs. You can define additional views too, but you will need to implement a couple methods to hook them up.
## Admin cards
TODO
## Admin forms
TODO
## List `displays`
On admin list views, you can define different `displays` to build predefined views of your data. The display choices will be shown in the UI, and you can use the current `self.display` in your view.
```python
# app/users/admin.py
from plain.admin.views import AdminModelListView, register_viewset
from .models import User
@register_viewset
class UserAdmin(AdminViewset):
class ListView(AdminModelListView):
model = User
fields = [
"id",
"email",
"created_at__date",
]
displays = ["Users without email"]
def get_objects(self):
objects = super().get_objects()
if self.display == "Users without email":
objects = objects.filter(email="")
return objects
```
## Toolbar
TODO
## Impersonate
TODO